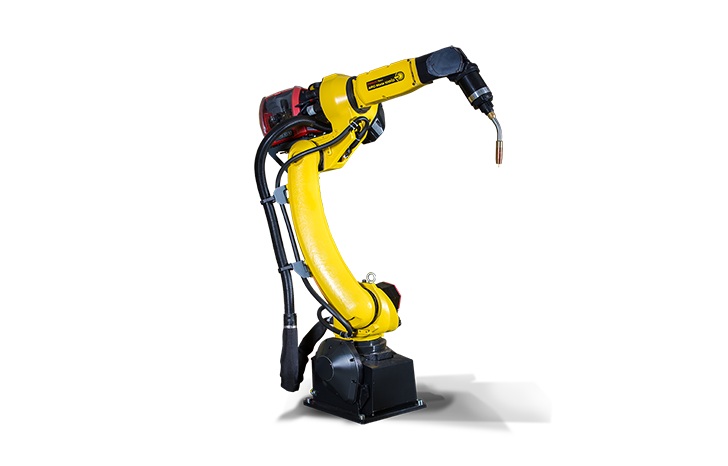
Six-axis robots, a subtype of articulated robots, have become the cornerstone of modern industrial automation. These versatile machines offer unparalleled flexibility, strength, and precision, making them an ideal solution for various applications such as welding automation, material handling, material removal, and painting. Their ability to perform complex movements across multiple planes makes them indispensable for streamlining production processes.
What Makes a Six-Axis Robot Unique?
Six-axis robots are characterized by their capacity to move along three linear axes (x, y, and z) and execute three rotational movements: roll, pitch, and yaw. This combination of movements mimics the dexterity of a human arm, enabling them to perform intricate tasks with precision. Each axis of the robot represents a unique degree of freedom, allowing it to move to specific programmed points with accuracy.
Detailed Movements of Each Axis
Axis One
Located at the base of the robot, Axis One allows the arm to pivot left and right across a 180-degree range. This fundamental movement enables the robot to transport objects in a straight line, providing the foundation for precise and efficient motion.
Axis Two
Controlling the robot’s lower arm, Axis Two facilitates forward and backward extensions. This axis enables vertical and horizontal movements, allowing the robot to lift, move, and place objects along the x or y planes seamlessly.
Axis Three
Axis Three empowers the robot’s upper arm to move up and down, significantly expanding its vertical reach. This axis enhances accessibility, allowing the robot to interact with parts across all three planes (x, y, and z) effectively.
Axis Four
Axis Four governs the roll motion of the robot’s upper arm. This movement allows the end-of-arm tooling (EOAT) to rotate, providing greater control over the orientation of objects and enabling precision in tasks such as assembly or welding.
Axis Five
Collaborating with Axis Four, Axis Five manages pitch and yaw movements. Pitch involves moving the EOAT up and down, while yaw facilitates left-to-right motion. This dual-axis control ensures the end-effector can adjust to complex angles and positions.
Axis Six
As the robot’s wrist, Axis Six is responsible for complete 360-degree rotations. This axis offers unmatched flexibility by enabling roll, pitch, and yaw movements, allowing the robot to orient parts precisely in all three dimensions.
Advantages of Six-Axis Robots
Six-axis robots provide several key advantages that make them a preferred choice in industrial automation:
- Enhanced Flexibility: With six degrees of freedom, these robots can handle intricate tasks that require precise positioning and orientation, mimicking human arm movements.
- Wide Application Range: They can perform a variety of tasks such as welding, painting, assembly, and material handling, making them highly versatile.
- Space Efficiency: Their compact design allows them to operate in confined spaces, optimizing factory layouts.
- Increased Productivity: By automating repetitive tasks, six-axis robots significantly boost production speed and efficiency, reducing lead times.
- Improved Accuracy and Consistency: These robots deliver precise, repeatable movements, ensuring consistent quality in production processes.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Over time, six-axis robots reduce labor costs and minimize errors, leading to long-term savings.
- Adaptability to Harsh Environments: Specialized models can operate in extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or cleanroom settings, ensuring reliability across various industries.
- Future-Proof Technology: Their ability to integrate with advanced software and systems, such as AI and IoT, ensures they remain relevant in evolving industrial landscapes.
Applications and Variants of Six-Axis Robots
The adaptability of six-axis robots makes them suitable for a wide range of applications. They are available in various sizes, from compact models like the FANUC LR Mate 200id to larger options such as the M-2000ia. Payload capacities range from a few kilograms to over a thousand kilograms, catering to diverse industrial needs. Additionally, specialized variants are designed for specific environments, such as cleanrooms or harsh conditions, like the FANUC M-710ic with its high IP rating.
Leading Manufacturers of Six-Axis Robots
Renowned manufacturers like FANUC, Yaskawa Motoman, ABB, and KUKA offer an extensive portfolio of six-axis robots. These companies have continuously innovated to meet the evolving demands of industries worldwide, solidifying six-axis robots as a staple in automation.
The Future of Industrial Automation
As industries strive for greater efficiency and precision, six-axis robots continue to set the benchmark for robotic automation. Their ability to perform complex tasks with speed and accuracy ensures they remain at the forefront of technological advancement in manufacturing and beyond.